Dispensing machines play a critical role in modern industrial manufacturing. Whether used for sealing, bonding, thermal conductivity, fixation, waterproofing, or structural reinforcement, precise dispensing greatly affects product consistency and long-term reliability. With rapid technology upgrades, the market now offers dozens of dispensing equipment models—from basic manual dispensers to high-speed piezoelectric jetting systems.
This guide provides a complete technical overview to help factories understand dispensing machine working principles, classification, performance comparison, selection strategy, and the latest generation technological trends. The goal is to help enterprises avoid selection mistakes, reduce costs, and improve production efficiency.
The core operating process of a dispensing machine includes: glue storage → pressure/flow control → motion path planning → dispensing execution → glue placement → curing. Each stage requires stable coordination to ensure consistent dispensing volume and high precision. In industries such as electronics and automotive, small variations in dispensing volume can directly impact product reliability.
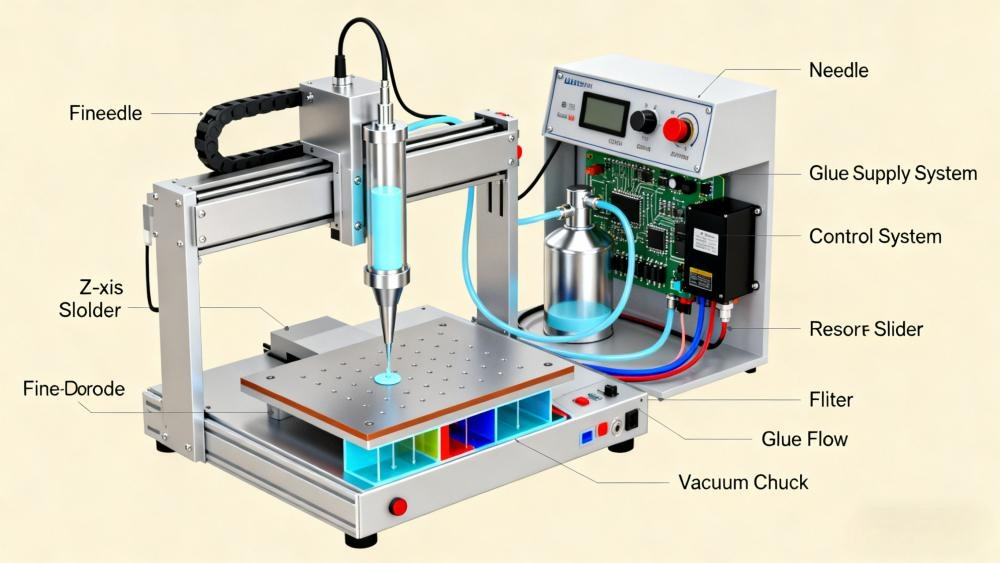

Dispensing equipment commonly uses servo or stepper motors. Servo motors provide higher torque, better repeatability (±0.01–0.02 mm), and faster response, suitable for high-precision manufacturing. Multi-axis systems (3-axis, 4-axis, 5-axis) execute linear, arc, or complex 3D paths.
Fluid control determines whether glue output is stable. Common mechanisms include:
CCD cameras recognize Mark points, patterns, and edges, enabling automatic correction during batch production. Visual calibration ensures long-term accuracy.
PLC + motion controller ensure synchronization. HMI interface supports CAD import, teaching programming, and real-time monitoring of glue flow parameters.
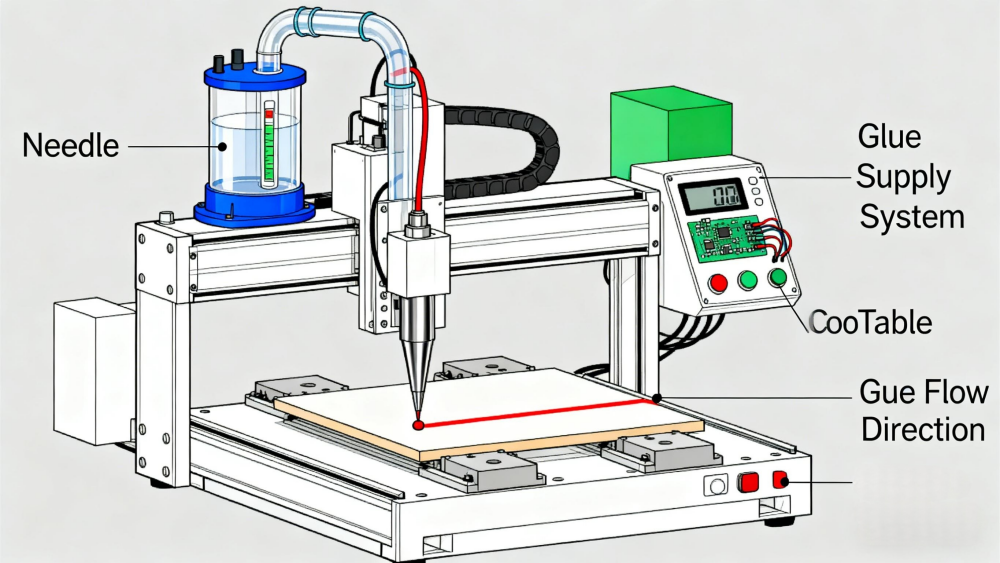
Used for fixed-position dot dispensing (0.1–5 mm diameter).
Produces straight lines, curves, irregular sealing paths (0.2–20 mm width).
Non-contact piezoelectric jetting, minimum spot 0.01 mm, suitable for micro electronics.
Single- or dual-component glues, accurate ratio control (±1%).
| Type | Advantages | Disadvantages | Application | Budget |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Manual Dispensing | Low cost, flexible, simple | Low precision, low consistency | Samples, repair | ¥1,000–¥5,000 |
| Jet Dispensing | Ultra-fast, non-contact, micro dots | Higher maintenance cost, viscosity sensitive | Chip packaging, sensors | ¥80,000–¥200,000 |
| Dual-Component Potting | Accurate mixing, high automation | Large size, complex cleaning | Power modules, chargers | ¥50,000–¥150,000 |
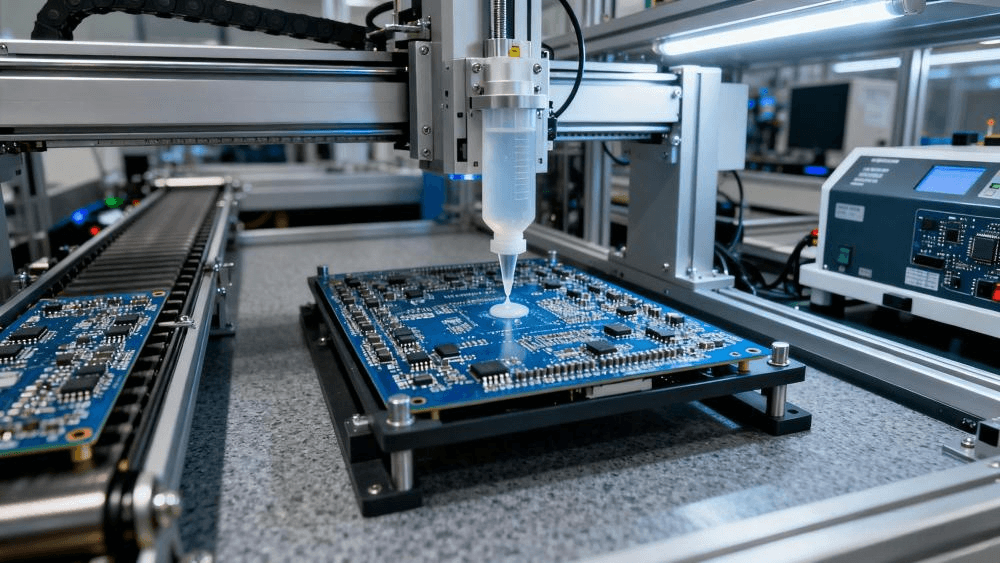
PCB thermal conductive glue, LED sealing, connector waterproofing, etc.
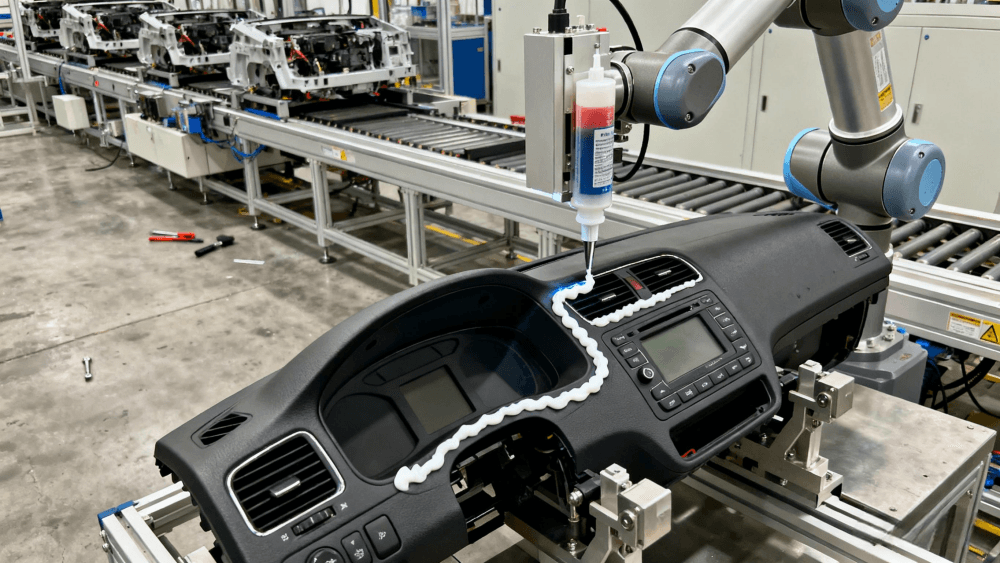
Headlight sealing, battery pack potting, dashboard bonding.
Solar frame sealing, energy storage module potting, EV chargers.

High-precision bonding in clean environments.
Toys, aerospace, packaging industry hot melt gluing.
Issue: Bubbles in glue
Solution: Vacuum degassing, check seals, reduce speed.
Issue: Glue amount unstable
Solution: Servo pressure control, glue temperature control, replace needle.
Issue: Position offset
Solution: Calibrate camera, improve fixture accuracy.
Issue: Needle clogging
Solution: Use anti-curing needle, choose correct diameter, clean immediately after stopping.
Selecting the correct dispensing machine requires balancing product requirements, production volume, cost, and technical capability. As technology evolves toward smart, flexible, and green manufacturing, choosing an advanced dispensing solution is essential for improving long-term competitiveness.
Founded in 2011, Shenzhen ZCX Technology Co., Ltd. is a professional manufacturer and solution provider specializing in glue dispensing machines and silicone extrusion equipment. We integrate design, development, consultation, production, and technical support, offering customers reliable and customized dispensing solutions. As a leading supplier in China, we are committed to delivering global value and supporting our clients with strong engineering capabilities and excellent service.
Looking for a high-precision, stable, and durable dispensing machine?
Contact ZCX Technology today for an expert consultation and customized solution.